Thursday, November 17, 2022
In this post, we have given a small script to convert BINARY data to BASE64 encoded data.
Before seeing the script, lets have a quick background,
Background: We have some binary data that we want to send across a network. Let's assume, we send them as bits and bytes over the network in a raw format.
Possibility 1: Few combinations of Binary data may be considered as control characters by the intermediate hardware components. (modem). This will result Unexpected behaviour.
Possibility 2: Binary data could be corrupted because the underlying protocol might think that you've entered a special character combination (like how FTP translates line endings).
So, to avoid all these, people encode the binary data into characters. Base64 is one of these types of encodings.
Script:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION convert_blob_to_base64(pic_blob IN BLOB) RETURN CLOB IS lc_clob CLOB; ln_chunk_size PLS_INTEGER := 24000; BEGIN FOR i IN 0..TRUNC((DBMS_LOB.GETLENGTH(pic_blob) - 1 ) / ln_chunk_size) LOOP lc_clob := lc_clob || UTL_RAW.CAST_TO_VARCHAR2 ( UTL_ENCODE.BASE64_ENCODE ( DBMS_LOB.SUBSTR( pic_blob, ln_chunk_size, i * ln_chunk_size + 1 ) ) ); END LOOP; RETURN lc_clob; END convert_blob_to_base64;
Thursday, November 17, 2022 by Team search · 0
Saturday, October 15, 2022
Query to check whether file exists on server using Oracle PLSQL (DBMS_LOB.FILEEXISTS, UTL_FILE.FGETATTR)
In this post, we have given few approaches to check whether file exists in the directory or not using PLSQL.
Background:
1. Create a Directory in the server and place the test file
2. Create a DBA_DIRECTORY for the same
Option 1: Using SQL query and DBMS_LOB.FILEEXISTS and BFILENAME
SELECT (CASE DBMS_LOB.FILEEXISTS(BFILENAME('TESTORACLE','test.dat')) WHEN 1 THEN 'FILE_EXISTS' ELSE 'FILE NOT FOUND' END ) testfile, (CASE DBMS_LOB.FILEEXISTS(BFILENAME('TESTORACLE','random.dat')) WHEN 1 THEN 'FILE_EXISTS' ELSE 'FILE NOT FOUND' END ) randomfile FROM dual;
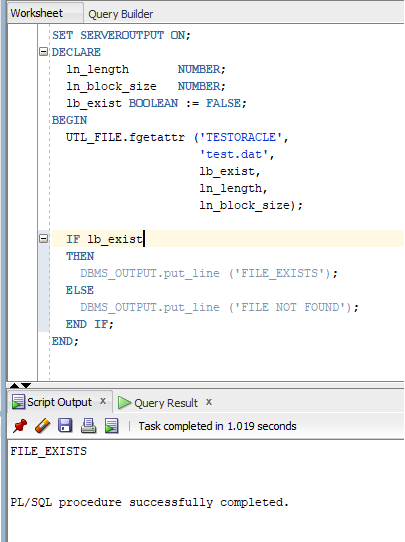
Option 2: Using PLSQL and UTL_FILE.FGETATTR function
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON; DECLARE ln_length NUMBER; ln_block_size NUMBER; lb_exist BOOLEAN := FALSE; BEGIN UTL_FILE.fgetattr ('TESTORACLE', 'random.dat', lb_exist, ln_length, ln_block_size); IF lb_exist THEN DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line ('FILE_EXISTS'); ELSE DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line ('FILE NOT FOUND'); END IF; END;
Saturday, October 15, 2022 by Team search · 1
Tuesday, December 8, 2020
Query to get system property (OS name, OS Architecture, OS Version, Oracle Home) and values of environment variables of database server in PLSQL - java.lang.System.getProperty & java.lang.System.getenv
In this post, we have given a PLSQL functions which inturn uses the standard Java function to gather the database tier OS level parameters and environment variable details.
Custom Functions:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION get_system_property(prop IN VARCHAR2) RETURN VARCHAR2 AUTHID DEFINER IS LANGUAGE JAVA name 'java.lang.System.getProperty(java.lang.String) return java.lang.String';
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION get_env_var_path(prop IN VARCHAR2) RETURN VARCHAR2 AUTHID DEFINER IS LANGUAGE JAVA name 'java.lang.System.getenv(java.lang.String) return java.lang.String';
Query:
SELECT get_system_property('user.dir') AS oracle_home, get_system_property('os.name') AS os_name, get_system_property('os.arch') AS os_architecture, get_system_property('os.version') AS os_version, get_system_property('user.name') AS user_name, get_system_property('user.home') AS user_home_directory, get_system_property('user.dir') AS user_curr_dir, get_system_property('java.vm.version') AS jvm_version, get_system_property('java.home') AS JAVA_HOME FROM dual;
SELECT get_env_var_path('ORACLE_HOME') AS "$ORACLE_HOME", get_env_var_path('CONTEXT_FILE') AS "$CONTEXT_FILE", get_env_var_path('HOSTNAME') AS "$HOSTNAME" FROM dual;System Properties (Quick Reference):
- java.version (Java Runtime Environment version)
- java.vendor (Java Runtime Environment vendor)
- java.vendor.url (Java vendor URL)
- java.home (Java installation directory)
- java.vm.specification.version (Java Virtual Machine specification version)
- java.vm.specification.vendor (Java Virtual Machine specification vendor)
- java.vm.specification.name (Java Virtual Machine specification name)
- java.vm.version (Java Virtual Machine implementation version)
- java.vm.vendor (Java Virtual Machine implementation vendor)
- java.vm.name (Java Virtual Machine implementation name)
- java.specification.version (Java Runtime Environment specification version)
- java.specification.vendor (Java Runtime Environment specification vendor)
- java.specification.name (Java Runtime Environment specification name)
- java.class.version (Java class format version number)
- java.class.path (Java class path)
- java.library.path (List of paths to search when loading libraries)
- java.io.tmpdir (Default temp file path)
- java.compiler (Name of JIT compiler to use)
- os.name (Operating system name)
- os.arch (Operating system architecture)
- os.version (Operating system version)
- file.separator (File separator ("/" on UNIX))
- path.separator (Path separator (":" on UNIX))
- line.separator (Line separator ("\n" on UNIX))
- user.name (User's account name)
- user.home (User's home directory)
- user.dir (User's current working directory)
Tuesday, December 8, 2020 by Team search · 0
Friday, November 20, 2020
Copy Files from one directory to another directory in PLSQL ( UTL_FILE.FCOPY, DBMS_LOB.FILEEXISTS example )
In this post, we have given a custom function which uses UTL_FILE.FCOPY to copy files from one directory to another directory. Further, custom function has below additional validations to check
- Source DBA directory is valid or invalid
- Destination DBA directory is valid or invalid
- source directory exists in server
- destination directory
exists in server
- source file exists or not.
- Override of destination file is allowed based on user parameters
This function can be further expanded with other validations and utilized for file copy operations. Hope this is useful :)
Standard Utility Used: UTL_FILE.FCOPY and DBMS_LOB.FILEEXISTS
Custom Copy Function:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION FILECOPY (p_source_directory IN VARCHAR2, p_source_filename IN VARCHAR2, p_dest_directory IN VARCHAR2, p_dest_filename IN VARCHAR2, p_override_allowed IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT 'N' ) RETURN VARCHAR2 AS lb_file_exists BOOLEAN; ln_dummy NUMBER; ln_file_size NUMBER; ln_block_size NUMBER; BEGIN --Check whether source directory exists BEGIN ln_dummy:= 0; SELECT 1 INTO ln_dummy FROM all_directories WHERE directory_name = p_source_directory; EXCEPTION WHEN NO_DATA_FOUND THEN RETURN 'Source DBA Directory Does not exists'; END; -- Check whether the directory present in server IF DBMS_LOB.FILEEXISTS(BFILENAME(p_source_directory,'.')) <> 1 THEN RETURN 'Source Directory Does not exists'; END IF; --Check whether destination directory exists BEGIN ln_dummy:= 0; SELECT 1 INTO ln_dummy FROM all_directories WHERE directory_name = p_dest_directory; EXCEPTION WHEN NO_DATA_FOUND THEN RETURN 'Destination DBA Directory Does not exists'; END; -- Check whether the directory present in server IF DBMS_LOB.FILEEXISTS(BFILENAME(p_dest_directory,'.')) <> 1 THEN RETURN 'Destination Directory Does not exists'; END IF; --Check whether source file exists IF DBMS_LOB.FILEEXISTS(BFILENAME(p_source_directory,p_source_filename)) <> 1 THEN RETURN 'Source File Does not exists'; END IF; --Check whether source file exists IF DBMS_LOB.FILEEXISTS(BFILENAME(p_dest_directory,p_dest_filename)) = 1 AND p_override_allowed = 'N' THEN RETURN 'Destination File Override is not allowed. But, destination file exists'; END IF; BEGIN UTL_FILE.FCOPY (p_source_directory, p_source_filename, p_dest_directory, p_dest_filename ); --Check whether destination file created IF DBMS_LOB.FILEEXISTS(BFILENAME(p_dest_directory,p_dest_filename)) = 1 THEN RETURN 'File Copied Successfully'; ELSE RETURN 'File Copy Failed. Please contact technical team'; END IF; EXCEPTION WHEN UTL_FILE.WRITE_ERROR THEN RETURN 'Destination Write/File Access denied'; WHEN UTL_FILE.READ_ERROR THEN RETURN 'Source Directory/File Access denied'; WHEN UTL_FILE.INVALID_OPERATION THEN -- This is true because we already checked other possible errors like -- source dir, destination dir , source file and dest file exists -- since above errs was not found, its assumed that access issue RETURN 'Directory/File Access denied'; WHEN OTHERS THEN RETURN SQLERRM; END; END FILECOPY;Sample Call to copy Function:SET SERVEROUTPUT ON; DECLARE lv_file_copy_sts VARCHAR2(2000); BEGIN lv_file_copy_sts := FILECOPY(p_source_directory => 'TEST1', p_source_filename => 'testfile.txt', p_dest_directory => 'TEST2', p_dest_filename => 'test.txt', p_override_allowed => 'Y' ); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('File copy Status: '||lv_file_copy_sts); END;
Sample runs to copy Function:
Friday, November 20, 2020 by Team search · 0
Query to get list of month and year since specific date in Oracle (Hierarchical queries - CONNECT BY Example)
In this post, we have given a query which will help you to get the list of months with year information since specific date.
For example, below query will get months and year in format of JAN-2019, FEB-2019 till today.
Query:
SELECT TO_CHAR(ADD_MONTHS(SYSDATE,((LEVEL-1)*-1)),'MON-RRRR') mon_yyyy FROM dual CONNECT BY ADD_MONTHS(SYSDATE,((LEVEL-1)*-1)) > TO_DATE('01-01-2019','MM-DD-RRRR') ORDER BY LEVEL;
Sample Run:
by Team search · 0